OVARIAN CYST LAPAROSCOPY PROCEDURE
Laparoscopy for Ovarian Cysts: A Modern Approach to Women’s Health
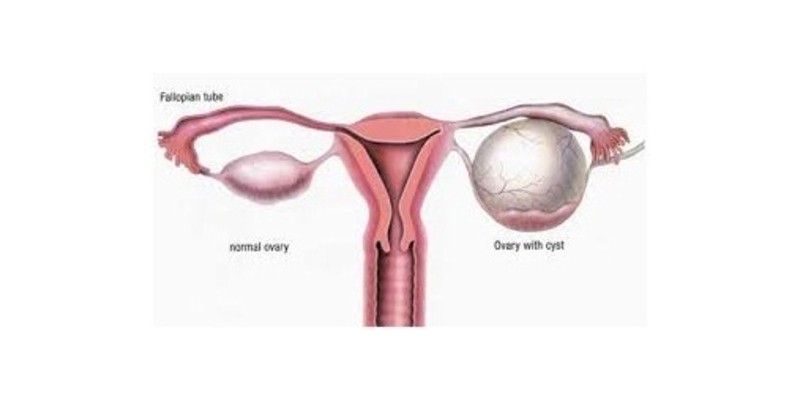
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs or pockets that develop in or on the ovaries. While most ovarian cysts are harmless and resolve on their own, some may grow larger, cause discomfort, or pose risks to a woman’s health. In such cases, surgical intervention may be required. Laparoscopy, a minimally invasive surgical technique, has revolutionized the management of ovarian cysts, offering precision, safety, and faster recovery for patients.
This blog delves into the details of laparoscopic management of ovarian cysts, from understanding their causes and symptoms to exploring the procedure, recovery, and potential benefits.
What Are Ovarian Cysts?
Ovarian cysts are common and often occur as part of the normal menstrual cycle. They can be broadly categorized into two types:
1. Functional Cysts
These are the most common type and are usually harmless. They form as a result of normal ovulation and often resolve without treatment. Subtypes include:
- Follicular Cysts: Form when the follicle doesn’t release an egg and continues to grow.
- Corpus Luteum Cysts: Develop after the follicle releases an egg and accumulates fluid.
2. Pathological Cysts
These cysts are unrelated to the menstrual cycle and may require medical intervention. Types include:
- Dermoid Cysts: Contain tissues like hair, skin, or teeth.
- Endometriomas: Caused by endometriosis, where uterine lining tissue grows on the ovaries.
- Cystadenomas: Develop from ovarian tissue and can grow large.
Symptoms of Ovarian Cysts
While many ovarian cysts are asymptomatic, larger or problematic cysts may cause:
- Pelvic pain, often on one side
- Bloating or abdominal discomfort
- Irregular menstrual cycles
- Pain during intercourse
- Frequent urination or difficulty emptying the bladder
- Sudden, severe pain (in case of rupture or torsion)
When Is Laparoscopy Recommended?
Laparoscopic surgery is considered for ovarian cysts in the following scenarios:
- Persistent Cysts: Cysts that do not resolve after several menstrual cycles.
- Large Cysts: Those exceeding 5-10 cm in size.
- Symptomatic Cysts: Causing pain, bloating, or menstrual irregularities.
- Suspicion of Malignancy: Cysts with irregular features on imaging studies.
- Torsion or Rupture: Emergency situations requiring immediate intervention.
Preparing for Laparoscopic Surgery
Preoperative Evaluation
A comprehensive evaluation is crucial to ensure the safety and success of the procedure:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: To assess overall health and symptoms.
- Imaging Studies: Ultrasound or MRI to evaluate the size, location, and characteristics of the cyst.
- Blood Tests: Including tumor markers (e.g., CA-125) to rule out malignancy.
- Pregnancy Test: To exclude ectopic pregnancy as a cause of symptoms.
Patient Preparation
- Fasting: Avoid food and drinks for 8-12 hours before surgery.
- Medications: Adjustments to medications, such as anticoagulants, may be necessary.
- Informed Consent: Detailed discussion about the procedure, risks, and benefits with the surgical team.
The Laparoscopic Procedure
1. Anesthesia
The surgery is performed under general anesthesia, ensuring the patient is comfortable and pain-free.
2. Incision and Laparoscope Insertion
- A small incision is made near the navel.
- A laparoscope—a thin, lighted tube with a camera—is inserted to visualize the pelvic organs on a monitor.
- Additional small incisions may be made for surgical instruments.
3. Removal of the Cyst
- The cyst is carefully separated from the ovary using specialized instruments.
- If possible, the healthy ovarian tissue is preserved.
- In cases where the cyst is suspected to be cancerous, the entire ovary may be removed to prevent spread.
4. Closure
- The surgical sites are closed with sutures or surgical glue.
- The patient is moved to a recovery room for monitoring.
Benefits of Laparoscopy for Ovarian Cysts
Compared to open surgery, laparoscopy offers numerous advantages:
- Minimally Invasive: Small incisions lead to reduced tissue trauma.
- Quicker Recovery: Most patients resume normal activities within 1-2 weeks.
- Reduced Pain: Less postoperative discomfort compared to traditional surgery.
- Lower Risk of Complications: Minimal blood loss and reduced risk of infection.
- Preservation of Fertility: Healthy ovarian tissue is often preserved, maintaining reproductive potential.
- Improved Cosmetic Outcomes: Smaller, less noticeable scars.
Postoperative Recovery
Immediate Recovery
- Patients are monitored for a few hours post-surgery.
- Pain relief medications are provided to manage discomfort.
- Light activities, such as walking, are encouraged to prevent blood clots.
At Home
- Rest and Recovery: Most patients can resume normal activities within 1-2 weeks, but strenuous activities should be avoided for 4-6 weeks.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Regular check-ups ensure proper healing and address any concerns.
- Managing Side Effects: Mild bloating, spotting, or discomfort may occur but usually resolve quickly.
Risks and Complications
While laparoscopy is generally safe, potential risks include:
- Bleeding: Excessive blood loss during or after surgery.
- Infection: Rare and treatable with antibiotics.
- Organ Injury: Accidental damage to nearby structures, such as the bladder or bowel.
- Adhesions: Scar tissue formation that could lead to pain or fertility issues.
- Cyst Recurrence: New cysts may develop in the future.
Fertility and Ovarian Health After Surgery
Laparoscopic management of ovarian cysts often preserves fertility and ovarian function. Women planning to conceive should discuss their options and timeline with their healthcare provider. In most cases, normal ovarian function resumes within a few weeks post-surgery.
Conclusion
Laparoscopic surgery for ovarian cysts is a groundbreaking approach that combines efficacy, safety, and patient comfort. By offering a minimally invasive solution, it addresses the challenges posed by ovarian cysts while promoting quicker recovery and preserving reproductive health. If you are experiencing symptoms related to ovarian cysts or have concerns about your ovarian health, consult a qualified gynecologist to explore whether laparoscopy is the right choice for you.
Advancements in laparoscopic techniques continue to empower women with safer, more effective options for managing their gynecological health, ensuring better outcomes and an enhanced quality of life.

