Tubal Cannulation
Hysteroscopic Tubal Cannulation for Tubal Block: A Revolutionary Approach in Infertility Treatment
Tubal blockages are one of the leading causes of infertility in women, preventing the fertilized egg from reaching the uterus. For decades, invasive surgeries were the primary option to treat such conditions. However, advancements in medical technology have introduced less invasive methods like hysteroscopic tubal cannulation, offering new hope to women struggling with tubal blockages.
This blog explores the intricacies of hysteroscopic tubal cannulation, its benefits, procedure, recovery, and its transformative role in infertility treatment.
Understanding Tubal Blockage
The fallopian tubes are essential for natural conception, as they transport the egg from the ovaries to the uterus. When these tubes are blocked or obstructed, sperm cannot reach the egg, preventing fertilization. Tubal blockages are often classified as:
- Proximal Blockage: Obstruction at the part of the fallopian tube closest to the uterus.
- Distal Blockage: Obstruction at the end of the fallopian tube near the ovary.
Causes of Tubal Blockage
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): A common cause of scarring and adhesions in the tubes.
- Endometriosis: Can lead to tissue growth and blockages.
- Previous Surgeries: Scar tissue from pelvic or abdominal surgeries may obstruct the tubes.
- Ectopic Pregnancy: A prior ectopic pregnancy can damage the tubes.
- Congenital Abnormalities: Structural issues present from birth.
What Is Hysteroscopic Tubal Cannulation?
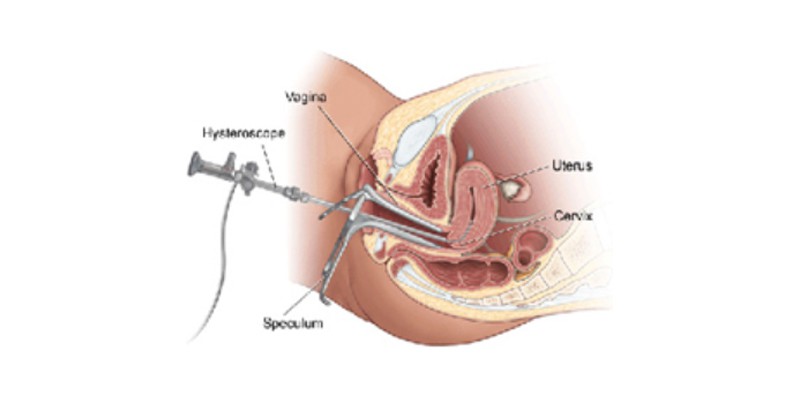
Hysteroscopic tubal cannulation is a minimally invasive procedure that uses a hysteroscope—a thin, lighted tube inserted through the cervix—to access and unblock the fallopian tubes. This technique is primarily used for proximal tubal blockages and is considered a first-line treatment before more invasive surgical options.
When Is Hysteroscopic Tubal Cannulation Recommended?
Hysteroscopic tubal cannulation may be advised in the following scenarios:
- Infertility Due to Proximal Tubal Blockage: Confirmed through imaging tests like hysterosalpingography (HSG) or sonohysterography.
- Unsuccessful Attempts at Conception: Despite normal ovulation and partner’s sperm health.
- Absence of Severe Pelvic Adhesions: For cases where the blockage is isolated to the proximal tube.
The Procedure: Step-by-Step
1. Preoperative Evaluation
- Medical History and Physical Examination: To determine overall health and suitability for the procedure.
- Imaging Tests: HSG or laparoscopy to confirm and locate the blockage.
- Blood Tests: To rule out infections or other medical conditions.
2. Preparing for the Procedure
- Fasting: Required for 8-12 hours before the procedure if general anesthesia is used.
- Medications: Antibiotics may be prescribed to reduce the risk of infection.
- Informed Consent: Patients are briefed about the procedure, risks, and benefits.
3. Performing Hysteroscopic Tubal Cannulation
- Anesthesia: The procedure is usually performed under local or general anesthesia, depending on patient preference and clinical indications.
- Hysteroscope Insertion: The hysteroscope is gently inserted through the cervix into the uterine cavity.
- Visualization: The uterine cavity and the openings of the fallopian tubes (tubal ostia) are visualized on a monitor.
- Guidewire Insertion: A thin guidewire or catheter is passed through the hysteroscope and into the blocked tube to clear the obstruction.
- Confirmation: A dye may be injected to confirm the patency of the tubes.
The entire procedure typically takes 30-60 minutes and is performed on an outpatient basis.
Benefits of Hysteroscopic Tubal Cannulation
Hysteroscopic tubal cannulation offers numerous advantages over traditional surgical methods:
- Minimally Invasive: No abdominal incisions are required, reducing tissue trauma.
- Outpatient Procedure: Patients can usually go home the same day.
- High Success Rates: Particularly effective for proximal blockages, with tubal patency rates of 70-90%.
- Faster Recovery: Most patients resume normal activities within a day or two.
- Improved Fertility Outcomes: Restoring tubal patency significantly enhances the chances of natural conception.
- Reduced Risks: Minimal blood loss and lower risk of complications compared to open surgery.
Post-Procedure Recovery
Immediate Recovery
- Patients are monitored for a few hours post-procedure to ensure there are no complications.
- Mild cramping or spotting may occur but typically resolves within a day.
At Home
- Rest: Patients are advised to rest for 24-48 hours.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers can alleviate mild discomfort.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Regular check-ups are essential to monitor recovery and discuss fertility plans.
Risks and Complications
While hysteroscopic tubal cannulation is generally safe, potential risks include:
- Infection: Rare and manageable with antibiotics.
- Tubal Perforation: Accidental injury to the tube, which is uncommon.
- Reblockage: The tubes may become blocked again over time.
- Ectopic Pregnancy: A small risk of ectopic pregnancy exists after the procedure.
Success Rates and Fertility Outcomes
The success of hysteroscopic tubal cannulation depends on several factors, including the cause and severity of the blockage. Studies report:
- Tubal Patency Rates: 70-90% for proximal blockages.
- Pregnancy Rates: 30-60% within 6-12 months post-procedure.
Women with successfully reopened tubes have significantly improved chances of natural conception.
Alternatives to Hysteroscopic Tubal Cannulation
If hysteroscopic tubal cannulation is unsuccessful or not feasible, other options include:
- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): Bypasses the fallopian tubes entirely.
- Tubal Surgery: Open or laparoscopic surgery to repair or bypass blockages.
- Selective Salpingography: A diagnostic and therapeutic procedure for proximal blockages.
Conclusion
Hysteroscopic tubal cannulation is a game-changing procedure for women facing infertility due to proximal tubal blockages. By offering a minimally invasive, safe, and effective solution, it restores hope to countless women aspiring to conceive naturally. If you are experiencing infertility due to tubal blockages, consult a fertility specialist to determine if hysteroscopic tubal cannulation is the right choice for you.
As medical technology continues to advance, procedures like this highlight the importance of personalized, patient-centered care in overcoming the challenges of infertility.

